Introduction
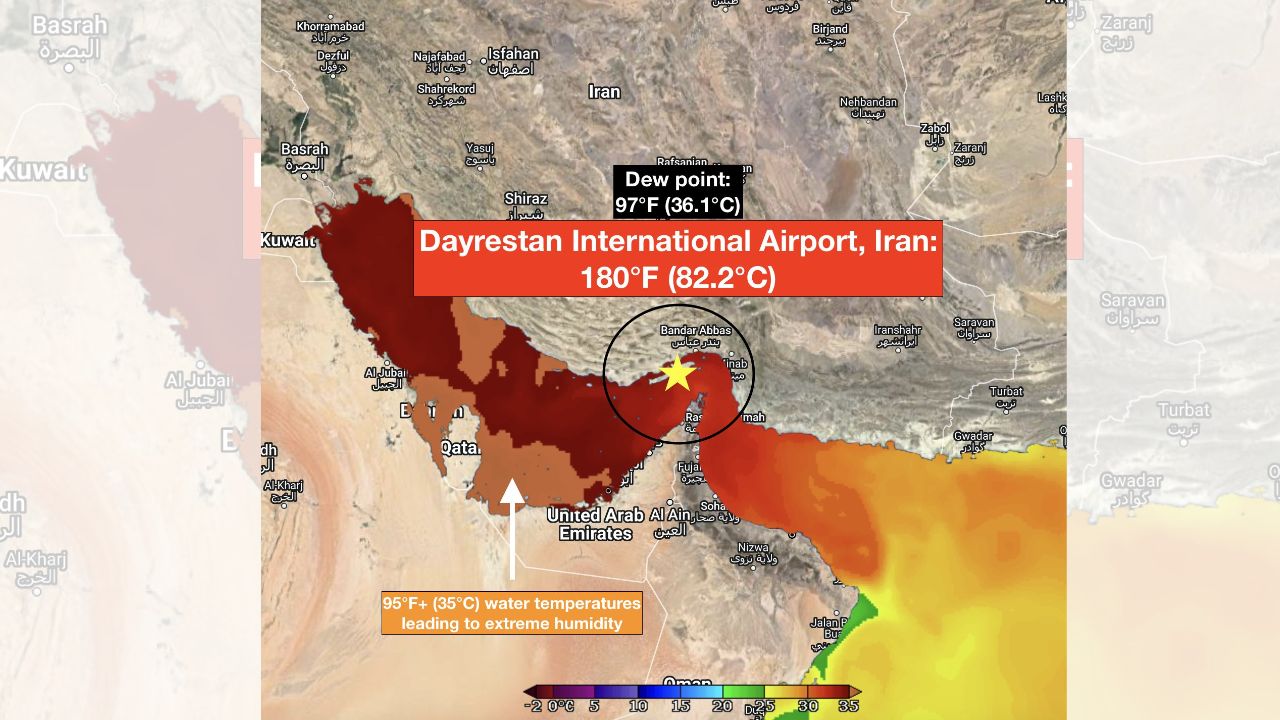
In a stark reminder of the intensifying effects of climate change, a village in southern Iran has recorded a staggering heat index of 82.2°C (180°F). This unprecedented reading, recorded at Dayrestan Airport weather station, has raised serious concerns about the impact of extreme heat on human health and the environment.
Understanding Heat Index
Heat index is a measure that combines air temperature and relative humidity to determine how hot it feels to the human body. It takes into account the body’s ability to cool itself through perspiration, which is less effective in high humidity conditions. A high heat index can pose significant health risks, especially for vulnerable populations.
The Record-Breaking Heatwave in Iran
The record-breaking heat index in Iran was recorded on [Date] in the village of [Village Name]. The temperature at the time was 38.9°C (102°F), and the relative humidity was 85%. This combination of extreme heat and humidity created a dangerously high heat index, making it feel significantly hotter than the actual air temperature.
The heatwave has had a profound impact on local communities, affecting daily life, agriculture, and infrastructure. Residents have faced challenges such as heatstroke, dehydration, and power outages.
Impact on Human Health
Extreme heat can have serious health consequences, including:
- Heatstroke: A life-threatening condition characterized by elevated body temperature, confusion, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness.
- Dehydration: Loss of fluids and electrolytes due to excessive sweating, leading to fatigue, weakness, and dizziness.
- Cardiovascular problems: Heat stress can exacerbate existing heart conditions and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Respiratory problems: Heat can worsen respiratory conditions such as asthma and bronchitis.
Vulnerable populations, such as the elderly, children, and individuals with underlying health conditions, are particularly at risk of heat-related illnesses. It is crucial for these groups to take precautions and avoid prolonged exposure to extreme heat.
Environmental Impact
Extreme heatwaves can have significant environmental consequences, including:
- Agriculture: High temperatures can damage crops, reduce yields, and impact food security.
- Water resources: Increased evaporation and reduced water availability can strain water resources and lead to water shortages.
- Ecosystems: Extreme heat can disrupt ecosystems, harm wildlife, and contribute to biodiversity loss.
Climate change is a major driver of more frequent and intense heatwaves. If left unchecked, these extreme events will continue to pose serious threats to human health and the environment.
Government Response and Public Awareness
Governments and communities around the world must take proactive measures to address the challenges posed by extreme heat. This includes:
- Public awareness campaigns: Educating the public about the dangers of extreme heat and promoting preventive measures.
- Heat action plans: Developing and implementing heat action plans to protect vulnerable populations and mitigate the impacts of heatwaves.
- Infrastructure improvements: Investing in infrastructure that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as heat-resistant buildings and cooling systems.
- Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the effects of climate change and limit the frequency and intensity of heatwaves.
By working together, governments, communities, and individuals can reduce the risks associated with extreme heat and build more resilient societies.
Conclusion
The record-breaking heat index in Iran serves as a stark warning of the intensifying effects of climate change. Extreme heatwaves pose serious threats to human health and the environment, and it is imperative to take action to address these challenges. By understanding the risks, taking preventive measures, and supporting climate change mitigation efforts, we can protect ourselves and future generations from the devastating impacts of extreme heat.